Hearing loss is a prevalent issue among a large population in the UK, thought to affect around 12 million people. By 2035, that number is estimated to rise to 14.2 million. Yet hearing loss is often an issue ignored by many, sometimes due to a lack of awareness about the condition and what can be done to help it. Understanding the different types of hearing loss and their symptoms can be a good place to start.
This blog will discuss the differences between sensorineural and conductive hearing loss and raise awareness of the importance of getting your hearing tested.

What is hearing loss?
As we mentioned above, there are two main types of hearing loss; sensorineural and conductive. But before discussing what they both are, we’ll look into the mechanism of hearing for a greater understanding of what is going on in our ears.
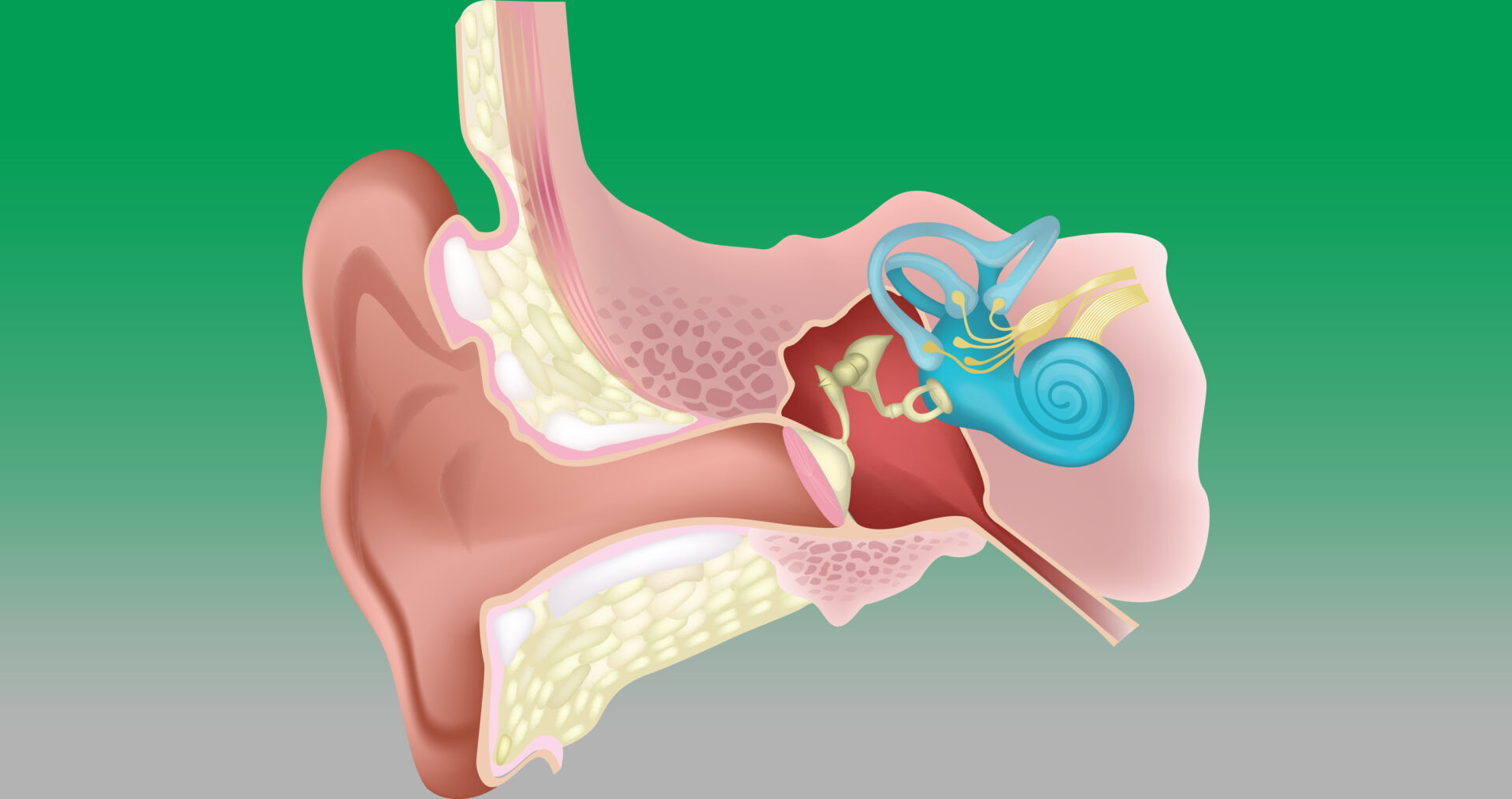
Firstly, how do we hear? At its simplest, the components of our ear convert sound waves from the air into electrical signals that our brain registers as sound.
To break this down:
- Firstly, sound waves enter our ears via the outer ear, travelling through the ear canal, and leading to the eardrum.
- Upon reaching the eardrum, this vibrates onto three tiny bones in our middle ear (the malleus, incus, and stapes)
- These three bones send the signal to the cochlea (the snail-shaped structure).
- The cochlea is filled with fluid, which once signalled will cause ripples, passing the vibrations to the basilar membrane.
- Here, tiny hair cells carry the signal and cause microscopic hair-like projections (stereocilia) to bounce off an overlying structure and bend, causing pore-like channels to open up.
- Chemicals rush into these cells which converts the signal into an electrical signal.
- Finally, the auditory nerve carries this electrical signal into the brain which then recognises it as sound. And voila, we can hear.
Now that we understand the mechanisms of hearing, we can look into the different kinds of hearing loss, and why they occur.
Sensorineural hearing loss
Sensorineural hearing loss is when damage occurs to the inner ear, primarily the cochlea or auditory nerve. It is usually the tiny hair cells in the cochlea that become damaged and no longer function in passing the vibrations through to the brain. Without these hairs, our brain can no longer register sound, resulting in total hearing loss.
This type of hearing loss typically tends to be a permanent loss of hearing and is unfortunately irreversible.
Causes of sensorineural hearing loss
The most common cause of sensorineural hearing loss is ageing. As we grow older, the general wear and tear that takes over our body also occurs in our ears. This means those tiny hair cells fail to regenerate like they once did, gradually reducing our hearing abilities.
Ageing isn’t the only risk factor for this type of hearing loss, however, as prolonged exposure to loud noises, genetic factors, and head trauma can also cause permanent damage to the structures in our ears.
Symptoms of sensorineural hearing loss
Some signs and symptoms to look out for with sensorineural hearing loss include:
- Difficulty hearing in noisy environments, such as a busy street or noisy bar.
- Difficulty following conversations when two or more people are talking
- Feelings of being dizzy or off-balanced
- Ringing or buzzing sound in your ears (known as tinnitus)
Conductive hearing loss
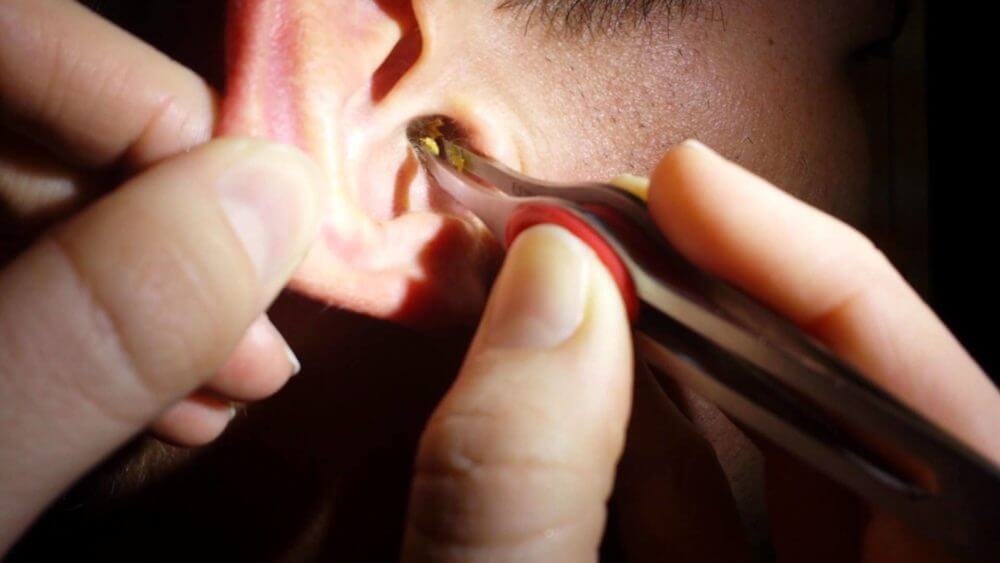
Now for conductive hearing loss. This kind of hearing loss results from issues with the middle or outer ear. Issues stemming from here cause problems with hearing as the sound waves can’t travel to the inner ear for the brain to register. Unlike sensorineural hearing loss, conductive hearing loss is often a temporary problem and more easily fixable.
Causes of conductive hearing loss
Conductive hearing loss can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Earwax blockages
- Ear infections
- Fluid in the middle ear
- Perforated eardrum
- Abnormalities in the ear structure
Symptoms of conductive hearing loss
The signs and symptoms of conductive hearing loss differ slightly from sensorineural hearing loss, which is why it is important to be aware of both kinds to help you identify which type of hearing loss you may be experiencing.
- Muffled hearing
- Dizziness
- Sudden loss of hearing
- ‘Stuffy’ sensation in your ear
- Pain or tenderness in the ear
Mixed hearing loss
Now that we’ve discussed both sensorineural and conductive hearing loss, it’s crucial to be aware of how they can combine to cause mixed hearing loss.
Mixed hearing loss occurs when there is a problem with both the outer/middle ear and the inner ear. It can be difficult to distinguish between the two types of hearing loss, especially if you are experiencing mixed hearing loss. If you believe you may have mixed hearing loss, it is important to have your hearing tested by a professional audiologist who can help diagnose the issue and provide treatment.
At Hearing Therapy, our team of expert audiologists are here to help you, providing a comprehensive hearing assessment to figure out the right course of action for your hearing.

Preventing hearing loss
As we’ve already found, some hearing loss is unfortunately out of our control. However, there are proactive steps we can take to protect our hearing.
If you are regularly exposed to prolonged loud noise, whether it be at work or in social environments, using ear protection can hugely reduce the impact on your hearing.
Seeking prompt medical attention for ear infections or ear abnormalities can also help solve the cause of your hearing loss. Healthcare professionals can provide medications or preventative measures so you don’t have to suffer.
Finally, regular hearing check-ups are the most effective way of preventing hearing loss from occurring. Those at higher risk of hearing loss, such as elderly people, those with genetic hearing issues, and those in prolonged noisy environments can benefit most from regular hearing assessments. Early detection allows for timely intervention and management of hearing-related issues.
Our hearing is one of our most important senses, playing a pivotal role in our everyday lives. Through understanding the different types of hearing loss, those suffering from the condition can more easily identify when they need to seek professional help and advice, ultimately aiming to improve their hearing and quality of life.
If you or someone you know is dealing with hearing loss, contact Hearing Therapy to make a booking, and help yourself to the joy of sound again.
